What Are Blockchain Forks and Why Do They Happen?
What Are Blockchain Forks and Why Do They Happen
Blockchain technology is often described as stable and unchangeable, but sometimes, major changes occur in the system — these are called forks.
In this blog, we’ll break down what blockchain forks are, why they happen, and what they mean for users and developers.
What is a Blockchain Fork?
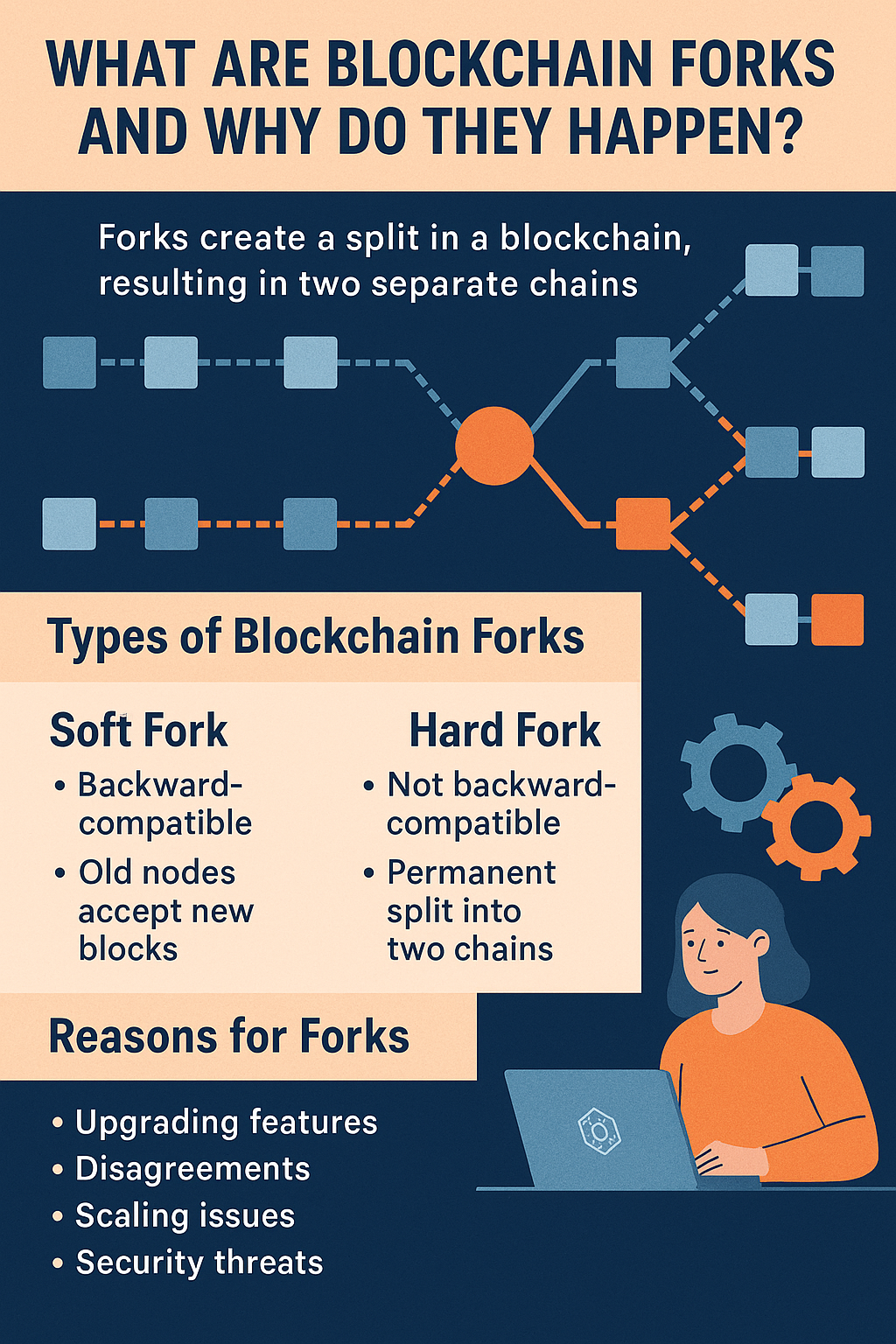
A fork in blockchain is a split that creates two separate paths forward. It occurs when participants in the network (called nodes) disagree on the rules that govern the blockchain. This disagreement can lead to the creation of a new blockchain with different features while the old one continues to exist.
There are mainly two types of forks:
- Soft Fork:
A soft fork is a backward-compatible upgrade. It means new rules are added, but old nodes (computers running the blockchain) can still recognize the new transactions. - Hard Fork:
A hard fork is not backward-compatible. It creates a permanent divergence from the old blockchain, often resulting in two different cryptocurrencies. A famous example is Bitcoin Cash being created from a Bitcoin hard fork.
Why Do Blockchain Forks Happen?
- Upgrading Features:
Developers may want to add new features, improve security, or fix bugs in the blockchain. - Disagreements:
If the community disagrees on how the blockchain should function, a fork may occur to allow both sides to continue their vision separately. - Scaling Issues:
Sometimes blockchains fork to handle more users or to speed up transactions (like Bitcoin’s block size debate). - Security Threats:
If vulnerabilities are found in a blockchain, an emergency fork may happen to fix them quickly.
Real-World Examples of Blockchain Forks
- Bitcoin Cash:
Created in 2017 after disagreements over Bitcoin’s scalability solutions. - Ethereum and Ethereum Classic:
In 2016, after a hack, Ethereum hard-forked to refund stolen funds, but some participants continued with the original chain (Ethereum Classic).
How Forks Affect Users
- Wallets and Exchanges:
After a fork, users might need to update their wallets or choose which blockchain they want to support. - New Coins:
Hard forks often give users free coins on the new blockchain if they held coins on the original chain. - Network Stability:
Initially, forks can cause confusion and volatility in coin prices.
Stay Stress-Free with Flutter Bees!
Feeling overwhelmed by the complexity of blockchain forks? Relax and have fun with the Flutter Bees Telegram mini app!
Flutter Bees helps you stay stress-free by letting you tap and enjoy a clicker game or defend your hive in an exciting defense game. Watching your hive grow increases points and helps you complete fun tasks! Give it a try and recharge your mind!
Would you also like the image for this topic now?
If yes, just say “Create image”!
Blockchain technology is often described as stable and unchangeable, but sometimes, major changes occur in the system — these are called forks.
In this blog, we’ll break down what blockchain forks are, why they happen, and what they mean for users and developers.
What is a Blockchain Fork?
A fork in blockchain is a split that creates two separate paths forward. It occurs when participants in the network (called nodes) disagree on the rules that govern the blockchain. This disagreement can lead to the creation of a new blockchain with different features while the old one continues to exist.
There are mainly two types of forks:
- Soft Fork:
A soft fork is a backward-compatible upgrade. It means new rules are added, but old nodes (computers running the blockchain) can still recognize the new transactions. - Hard Fork:
A hard fork is not backward-compatible. It creates a permanent divergence from the old blockchain, often resulting in two different cryptocurrencies. A famous example is Bitcoin Cash being created from a Bitcoin hard fork.
Why Do Blockchain Forks Happen?
- Upgrading Features:
Developers may want to add new features, improve security, or fix bugs in the blockchain. - Disagreements:
If the community disagrees on how the blockchain should function, a fork may occur to allow both sides to continue their vision separately. - Scaling Issues:
Sometimes blockchains fork to handle more users or to speed up transactions (like Bitcoin’s block size debate). - Security Threats:
If vulnerabilities are found in a blockchain, an emergency fork may happen to fix them quickly.
Real-World Examples of Blockchain Forks
- Bitcoin Cash:
Created in 2017 after disagreements over Bitcoin’s scalability solutions. - Ethereum and Ethereum Classic:
In 2016, after a hack, Ethereum hard-forked to refund stolen funds, but some participants continued with the original chain (Ethereum Classic).
How Forks Affect Users
- Wallets and Exchanges:
After a fork, users might need to update their wallets or choose which blockchain they want to support. - New Coins:
Hard forks often give users free coins on the new blockchain if they held coins on the original chain. - Network Stability:
Initially, forks can cause confusion and volatility in coin prices.
Stay Stress-Free with Flutter Bees!
Feeling overwhelmed by the complexity of blockchain forks? Relax and have fun with the Flutter Bees
Flutter Bees helps you stay stress-free by letting you tap and enjoy a clicker game or defend your hive in an exciting defense game. Watching your hive grow increases points and helps you complete fun tasks! Give it a try and recharge your mind!




Post Comment