Blockchain
Crypto
bee hive defense, blockchain explained, blockchain security, blockchain technology, blockchain transaction, clicker game, consensus mechanism, cryptographic hash, decentralized network, digital ledger, flutter bees, how blockchain works, proof of stake, proof of work, stress relief games, telegram mini app, web3
Akshay Thakur
0 Comments
How Does Blockchain Work?
Understanding the Technology Behind Decentralization
Blockchain is more than just a buzzword—it’s a game-changing technology that powers everything from cryptocurrencies to smart contracts. But how does it actually work under the hood? Let’s break it down in simple terms.
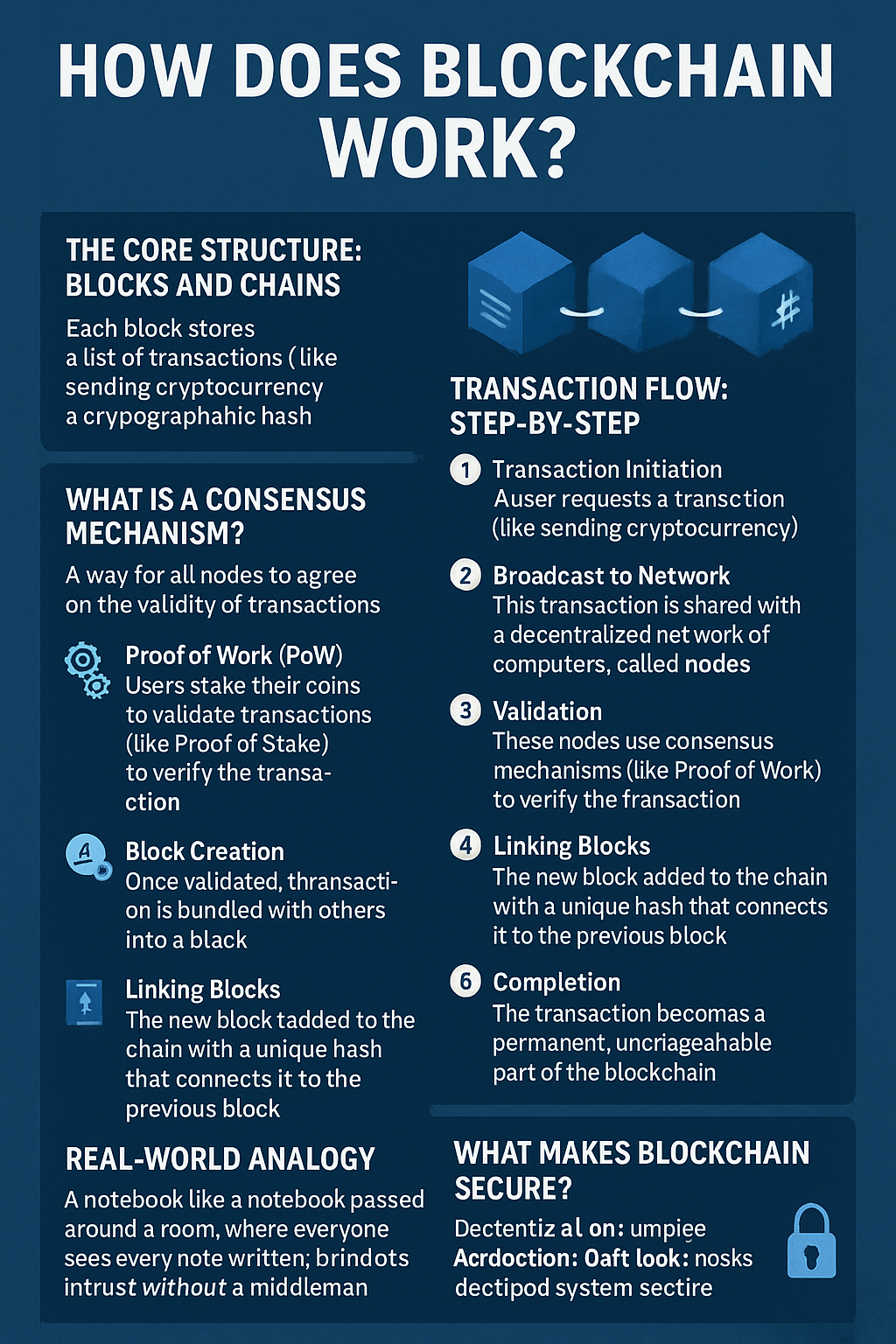
- The Core Structure: Blocks and Chains
At the heart of blockchain is a digital “chain” made of “blocks.” Each block stores:
A list of transactions
A timestamp
A cryptographic hash of the previous block
These blocks are linked together, creating a continuous, tamper-proof record—hence the name blockchain.
- Transaction Flow: Step-by-Step
Here’s what happens when someone makes a transaction on the blockchain:
- Transaction Initiation: A user requests a transaction (like sending cryptocurrency).
- Broadcast to Network: This transaction is shared with a decentralized network of computers, called nodes.
- Validation: These nodes use consensus mechanisms (like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake) to verify the transaction.
- Block Creation: Once validated, the transaction is bundled with others into a block.
- Linking Blocks: The new block is added to the chain with a unique hash that connects it to the previous block.
- Completion: The transaction becomes a permanent, unchangeable part of the blockchain.
- What is a Consensus Mechanism?
Since blockchain has no central authority, it needs a way for all nodes to agree on the validity of transactions. This is where consensus mechanisms come in:
Proof of Work (PoW): Miners solve complex math problems. First to solve it adds the block and earns rewards (used in Bitcoin).
Proof of Stake (PoS): Users stake their coins to validate transactions. More coins = higher chances to verify (used in Ethereum 2.0).
Other types include Delegated Proof of Stake, Proof of Authority, etc.
- What Makes Blockchain Secure?
Decentralization: No single point of failure.
Cryptographic Hashing: Each block is uniquely encoded.
Immutability: Once written, data can’t be altered without changing the entire chain.
Transparency: All transactions are publicly visible on the ledger.
- Real-World Analogy
Think of blockchain like a notebook passed around a room. Everyone sees every note written. If someone tries to alter a previous note, everyone will notice because their copy no longer matches. That’s how blockchain maintains trust without a middleman.
Conclusion
Blockchain works through a clever combination of cryptography, distributed networks, and consensus algorithms. It enables trustless transactions—where people can exchange value securely without needing to trust one another or a central authority.
Understanding how blockchain works is the first step to exploring its real-world applications in finance, healthcare, education, and beyond.
Take a Break with Flutter Bees – A Mini Game to Relax Your Mind
After diving into the technical side of blockchain, why not take a moment to unwind?
Try the Flutter Bees Telegram Mini App – a fun and stress-relieving game where you can:
Tap away stress in the Clicker Game
Defend your hive in the Bee Hive Defense Game
Watch and earn more points to complete exciting tasks
It’s a playful way to relax while keeping your mind engaged. Try it out now!
Would you like an image generated for this post as well?




Post Comment